Types of Screws and Their Working
A Simple Guide On Types of Screws and Their Working
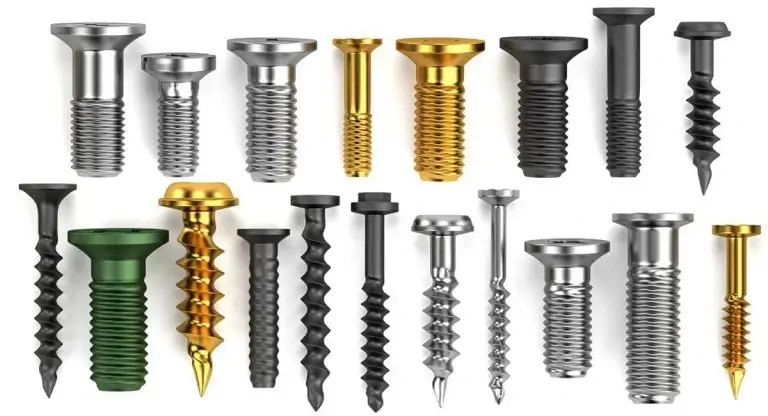

Screws are essential fasteners that play a crucial role in holding things together. From assembling furniture to constructing buildings, screws come in various types, each designed for specific applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of screws, their unique features, and how they work.
Key Components of a Screw
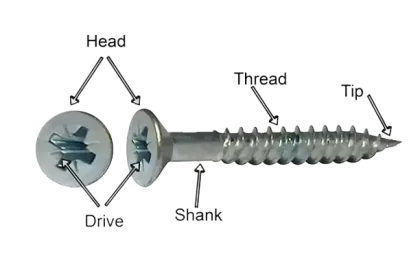
Before exploring the diverse world of screws, it's essential to grasp the fundamental components that make up these versatile fasteners. A screw consists of three main parts, each playing a crucial role in its functionality.
Head:
The head, positioned at the top of the screw, serves as the point of contact for turning tools such as screwdrivers or wrenches. It comes in various shapes, including flat, pan, round, and hexagonal, each designed for compatibility with specific tools. Some heads feature additional elements like slots or recesses, requiring specialized drivers. The choice of head type is often dictated by the desired finish and the tools available. Flat heads allow for flush installations, pan heads offer versatility, while hex heads provide increased torque for robust fastening.
Drive:
The drive, located within the head, is a crucial element that determines the type of tool required for turning the screw. It can take the form of various recesses or grooves, such as slotted, Phillips, Allen (hex), Torx, or square. The drive is an essential consideration, as the right tool ensures proper engagement and minimizes the risk of slippage during installation or removal.
Thread:
The thread, a helical groove spiraling around the screw's body, is the element responsible for gripping into the material. Threads come in various designs, with coarse threads offering enhanced grip in softer materials like wood, and fine threads providing precision and strength in harder materials like metal. The pitch and depth of the threads vary based on the screw type. The thread's design is pivotal for the screw's ability to securely hold materials together, making it a critical consideration when selecting screws for specific applications.
Shank:
The shank, constituting the central body of the screw excluding the head and thread, provides structural support and stability. Available in different diameters and lengths, the shank may be smooth or feature additional elements like grooves or ridges. The thickness and material of the shank significantly impact the overall strength of the screw. The characteristics of the shank play a vital role in determining the screw's load-bearing capacity. Thicker shanks are suitable for handling heavier loads, while longer shanks provide increased reach for specific applications.
Understanding the distinct features of the head, thread, and shank empowers individuals to make informed choices when selecting screws for various tasks. Whether engaged in woodworking, machinery assembly, or construction projects, a comprehensive knowledge of these key components ensures optimal performance and the creation of reliable connections.
Types of Screws:
Wood Screws

Wood screws are specialized fasteners designed for applications involving wood and wood-based materials. They are characterized by their coarse threads and are tailored to provide a secure and robust connection in wooden structures.
Features:
Coarse Threads: Designed with threads that have a larger pitch, providing better grip and holding power in wood.
Head Types: Typically equipped with flat or oval heads, allowing for easy countersinking, creating a smooth and flush finish.
Variety in Length and Gauge: Available in various lengths and gauges to accommodate different wood thicknesses and project requirements.
Applications:
Woodworking Projects: Ideal for constructing wooden furniture, cabinets, and other woodworking endeavors.
Furniture Assembly: Commonly used to join wooden components in the assembly of furniture pieces.
Deck Construction: Suited for fastening wooden planks and components in outdoor decking projects.
Machine Screws

Machine screws are versatile fasteners designed for use with nuts or threaded holes in machinery, equipment, and other mechanical applications. They are known for their precision and reliability in fastening components together.
Features:
Fine Threads: Engineered with threads of a smaller pitch, providing precise and secure fastening in metal or threaded holes.
Diverse Head Types: Available with various head types, including pan, flat, and round heads, catering to different application needs.
Used with Nuts: Often employed in conjunction with nuts to create a stable and secure connection.
Applications:
Machinery Assembly: Widely used for assembling mechanical components in machinery and equipment.
Electronics and Electrical Components: Suitable for securing components in electronic devices and electrical panels.
Automotive Applications: Utilized in the assembly of automotive parts and systems.
Sheet Metal Screws

Sheet metal screws are designed for fastening metal sheets and thin materials. They are characterized by sharp threads that can cut through and securely grip these materials, providing an effective solution for metal-to-metal connections.
Features:
Self-Tapping Ability: Capable of creating threads in metal without the need for pre-drilling, making installation efficient.
Pan or Flat Heads: Equipped with pan or flat heads for flush installation in sheet metal.
Variety in Length and Thread Styles: Available in different lengths and thread styles to accommodate various sheet metal thicknesses.
Applications:
HVAC Installations: Used to secure components in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Roofing Projects: Ideal for fastening metal roofing sheets and components.
Automotive Bodywork: Employed in automotive applications for attaching panels and body components.
Drywall Screws

Drywall screws are specifically designed for fastening drywall to wooden or metal studs. They are characterized by their coarse threads, which are intended to securely grip into the drywall material.
Features:
Coarse Threads for Drywall Grip: The threads are designed to penetrate and grip into drywall, providing a secure connection.
Bugle Heads: The heads have a bugle shape to prevent tearing of the paper covering the drywall during installation.
Variety in Length: Available in various lengths to accommodate different drywall thicknesses.
Applications:
Drywall Installation: Primary use is for attaching drywall sheets to wooden or metal studs in construction projects.
Interior Construction: Widely used in interior construction for fastening drywall in residential and commercial spaces.
Lag Screws

Lag screws, also known as lag bolts, are heavy-duty fasteners designed for robust applications, particularly for attaching heavy objects to wood. They are characterized by their thick and sturdy design.
Features:
Thick and Sturdy: Designed to provide a strong and durable connection, suitable for heavy loads.
External Hex Head: Equipped with an external hex head for easy installation using a wrench or socket.
Coarse Threads for Maximum Grip: The coarse threads enhance grip and stability when driven into wood.
Applications:
Securing Large Structures: Used in construction to secure large structures, such as beams, to wooden supports.
Building Decks and Fences: Commonly employed in deck and fence construction for attaching structural components.
Timber Framing: Used in timber framing projects where a strong connection is essential for structural integrity.
How Screws Work:

Threaded Engagement:
Screws work by creating a threaded engagement with the material they are driven into. The helical threads of the screw cut into the material, providing a strong and secure connection.
Turning Motion:
Screws are driven into the material by a turning motion applied to the head using a screwdriver, wrench, or other suitable tools. This turning motion advances the screw into the material.
Tension and Compression:
As the screw is turned, it exerts both tension and compression forces on the material. The threads pull the screw into the material (tension), while the head of the screw presses against the material (compression).
Pilot Holes:
For certain types of screws, especially those used in hard materials like metal or hardwoods, it's common to create pilot holes. These are smaller holes drilled into the material before driving the screw, providing a path for the screw to follow and reducing the likelihood of splitting or damage.
Countersinking:
In applications where a smooth and flush finish is desired, screws can be countersunk. This involves creating a conical recess in the material for the screw head to sit in, allowing it to be flush with or below the surface.
Tips for Choosing the Right Screw:
Material Compatibility:
Consider the material you are working with. Different screws are designed for use in wood, metal, or other materials. Choose a screw that is compatible with the material to ensure a secure and durable connection.
Length and Gauge:
Select the appropriate length and gauge of the screw based on the thickness of the materials being joined. Using the right size ensures optimal performance and strength.
Head Type:
The choice of head type depends on the application and the desired finish. For example, flat heads are ideal for countersinking, while pan heads are suitable for applications where a raised head is acceptable.
Thread Type:
Coarse threads are suitable for wood, while fine threads are better for metal and other hard materials. Consider the specific requirements of your project when choosing the thread type.
Corrosion Resistance:
For outdoor or damp environments, consider using screws with corrosion-resistant coatings or materials like stainless steel to prevent rust and degradation over time.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, screws are versatile fasteners with various types designed for specific applications. Understanding the different types of screws and their unique features is crucial for achieving strong and reliable connections in your projects. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional builder, choosing the right screw for the job ensures the success and longevity of your construction or assembly projects.
For more information on this blog or to learn more about fasteners, feel free to contact us. Termscript Fasteners, as leading fasteners manufacturers in Pune, our dedicated team is ready to guide you.




